News
Working temperature:
In addition to considering the maximum and minimum temperatures of the environment, do not forget the heat generated by the motor during operation. Sometimes, additional heat and elevated temperature can lead to a decrease in the performance of magnets, especially NdFeB magnets. For example, even at 50 ° C, the performance of N35 will be lower than that of N35M or N35H. To avoid potential issues, Siemens Gamesa has used N52H in some of its wind turbines. I hope more people will pay attention to the negligence in the selection of motor magnets.
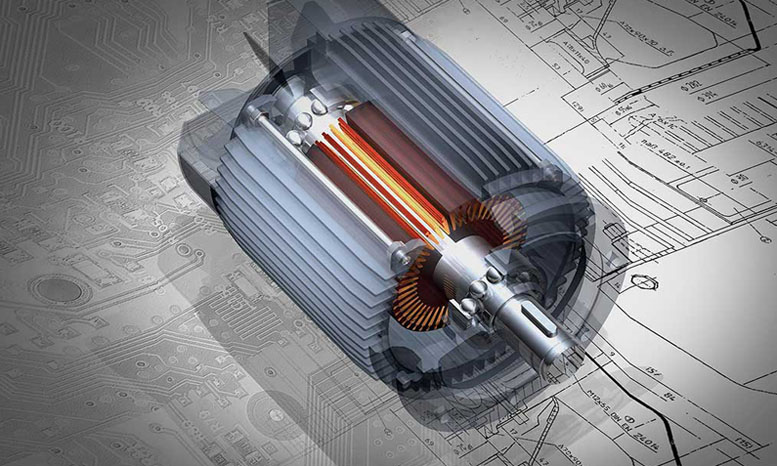
Corrosion resistance:
If your machine will be exposed to corrosive environments, please choose magnet materials with good corrosion resistance or consider applying protective coatings.
Application requirements
Power and torque:
Determine the power and torque requirements of the motor. Different magnetic materials provide varying levels of magnetic field strength, which directly affects performance.
Operating speed:
Consider the required operating speed of the machine. Some magnetic materials may be more suitable for high-speed applications, while others perform well in low-speed or high torque scenarios.
Size and weight:
Magnets come in various sizes and shapes. Choose the magnet size and configuration that fits your machine design limitations.
